Week 02 – Whole Numbers and Decimal Numbers, Multiples and Factors
What are Whole Numbers?
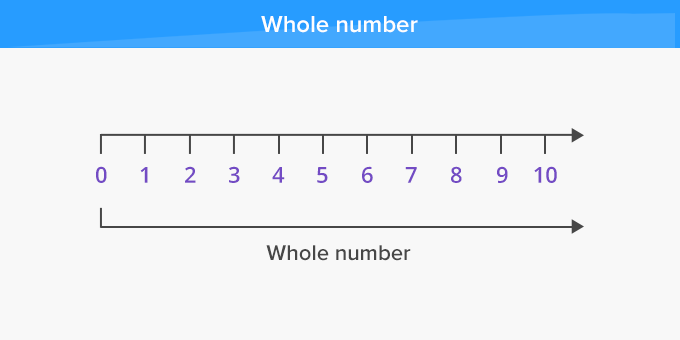
In mathematics, whole numbers are the basic counting numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, … and so on.
17, 99, 267, 8107 and 999999999 are examples of whole numbers.
Whole numbers include natural numbers that begin from 1 onwards.
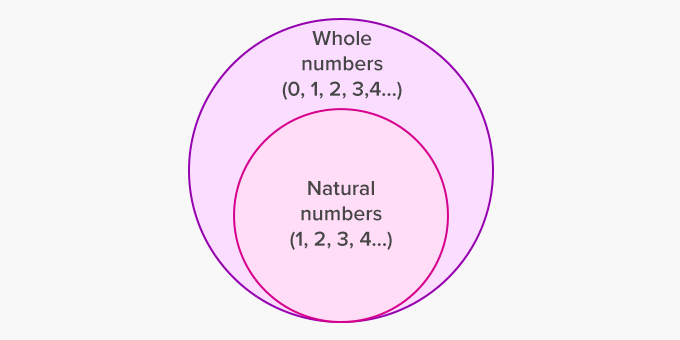
Whole numbers include positive integers along with 0.
What are Factors & Multiples
Factors and multiples are different things. But they both involve multiplication:
- Factors are what we can multiply to get the number
- Multiples are what we get after multiplying the number by an integer (not a fraction).
Example: the positive factors, and some multiples, of 6:
Factors:
- 1 × 6 = 6, so 1 and 6 are factors of 6
- 2 × 3 = 6, so 2 and 3 are factors of 6
Multiples:
- 0 × 6 = 0, so 0 is a multiple of 6
- 1 × 6 = 6, so 6 is a multiple of 6
- 2 × 6 = 12, so 12 is a multiple of 6
- and so on
(Note: there are negative factors and multiples as well)
Here are the details:
Factors
“Factors” are the numbers we can multiply together to get another number:
2 and 3 are factors of 6
A number can have many factors.
Example: 12
- 3 × 4 = 12, so 3 and 4 are factors of 12
- Also 2 × 6 = 12, so 2 and 6 are also factors of 12,
- And 1 × 12 = 12, so 1 and 12 are factors of 12 as well.
AND because multiplying negatives makes a positive, −1, −2, −3, −4, −6 and −12 are also factors of 12:
- (−1) × (−12) = 12
- (−2) × (−6) = 12
- (−3) × (−4) = 12
So ALL the factors of 12 are:
1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12
AND −1, −2, −3, −4, −6 and −12
Multiples
A multiple is the result of multiplying a number by an integer (not a fraction).
Example: Multiples of 3:
…, −9, −6, −3, 0, 3, 6, 9, …
Example: 15 is a multiple of 3, as 3 × 5 = 15
Example: 16 is not a multiple of 3
Example: Multiples of 5:
…, −15, −10, −5, 0, 5, 10, 15, …
Example: 10 is a multiple of 5, as 5 × 2 = 10
Example: 11 is not a multiple of 5



